- Details for Rubber Accelerator ZBEC
-
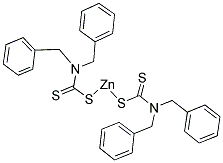
Rubber Accelerator ZBEC 14726-36-4
| Category : |
Polymers |
 |
| CAS NO : |
14726-36-4 |
| EC NO : |
238-778-0 |
| MF : |
C15H14NS2 |
| MW : |
272.4089 |
| Specification : |
Power Granules |
| Packing : |
Coextruded paper bags lined with polyethylene film bags. Net weight 25 kg per bag. |
| Product description : |
Item Specifications
Power dust suppressed Power Granules
Appearance White to light-cream Power( Granules)
Initial Melting Point, °C Min. 178 176 176
Heat Loss , % Max. 0.50 0.50 0.50
Zinc Content , % 10.0 - 11.5 9.8 - 11.3 10.0 - 11.5
Residue on 150 ?m Sieve , % Max. 0.10 0.10 -
Residue on 63 ?m Sieve , % Max. 0.50 0.50 -
Zinc Salt Soluble in water, % Max. 0.05 0.05 0.05
Addtitive,% - 1.0 - 2.0 0.5 - 1.5
White to light-cream Power , relative density is 1.14g/cm3 . melting point is above 178 °C. Soluble in alchohol,benzene,chloromethane ,insoluble in water. Storage is stable. |
| Uses : |
A overspead accelerator for natural and synthetic rubber and latex. Curing active temperature is low. It can substitute for ZDBC, ZDEC, PZ, ect .. Operating safety is much better. Specially , it will not produce cancer-causing nitrosamize during the rubbe |
| Synonyms : |
ZBEC;zinc dibenzyldithiocarbamate;dibenzyldithiocarbamic acid zinc salt;zinc bis(n,n-dibenzyldithiocarbamate);zinc dibenzyl dithiocarbamate;zbec;dibenzyldithiocarbamic acid, zn salt;benzyl zimate;zbdc;zinc n,n-dibenzyldithiocarbamate;bis[bis(phenylmethyl)carbamodithioato-s,s']-,(t-4)-zinc;s']-bis[bis(phenylmethyl)carbamodithioato-(beta-4)-zin;zinc,bis[bis(phenylmethyl)carbamodithioato-s,s']-,(t-4)-;zinc bis(dibenzyldithiocarbamate);n,n-dibenzyl dithiocarbamic acid zine salt;zinc, bisbis(phenylmethyl)carbamodithioato-.kappa.s,.kappa.s-, (t-4)-;bibenzyldithiocarbamicacidzincsalt;zinkbis(dibenzyldithiocarbamat);zinc (dibenzylamino)methanedithioate;bis[[(dibenzylamino)(thiocarbonyl)]thio] zinc;dibenzyldithiocarbamic acid zinc salt,95%;zinc bis(dibenzylcarbamodithioate);dibenzyldithiocarbamate;Zinc dibenzyldithiocarbamate; |
| Molecular Structure : |
 |

