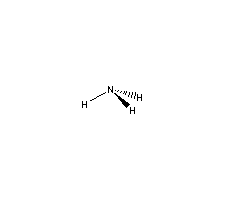
| Product description : |
| Ammonia Chemical Properties |
| mp | −78 °C(lit.)
| | bp | 60 °C
| | density | 1.023 g/mL at 25 °C
| | vapor density | 0.6 (vs air)
| | vapor pressure | 8.75 atm ( 21 °C)
| | Fp | 52 °F
| | storage temp. | 0-6°C | | Water Solubility | soluble | | Sensitive | Hygroscopic | | Merck | 14,492 | | Stability: | Stable. Hygroscopic. Flammable. Incompatible with acids, strong oxidizing agents. May react violently with acids, aldehydes, alkylene oxides, amides, boron, boron halides, calcium, chlorine azide, chloric acid, chlorine monoxide, chlorites, halogens, heavy metals and many other materials - check the complete data sheet before use! | | CAS DataBase Reference | 7664-41-7(CAS DataBase Reference) | | NIST Chemistry Reference | Ammonia(7664-41-7) | | EPA Substance Registry System | Ammonia(7664-41-7) |
| Ammonia Usage And Synthesis |
| Chemical Properties | colourless gas (standard conditions) | | Usage | Ammonia is a large-tonnage industrial product and finds its major use in the manufacture of nitric acid and fertilizers. It is the most commonly used refrigerant, particularly for large industrial installations. | | Usage | Ammonia is a large-tonnage industrial product and finds its major use in the manufacture of nitric acid and fertilizers. The aqueous solution is widely used in the chemical industry. | | Usage | Ammonia is a large-tonnage industrial product and finds its major use in the manufacture of nitric acid and fertilizer. The aqueous solution is widely used in the chemical industry, mostly as refrigerant. Product Data Sheet | | Usage | Reagent for chemical vapor deposition of TiN.1 | | Air & Water Reactions | Soluble in water with evolution of heat. The amount of heat generated may be large. | | Reactivity Profile | AMMONIA is a base. Reacts exothermically with all acids. Violent reactions are possible. Readily combines with silver oxide or mercury to form compounds that explode on contact with halogens. When in contact with chlorates Ammonia forms explosive ammonium chlorate [Kirk-Othmer, 3rd ed., Vol. 2, 1978, p. 470]. Reacts violently or produces explosive products with fluorine, chlorine, bromine and iodine and some of the interhalogen compounds (bromine pentafluoride, chlorine trifluoride). Mixing of bleaching powder (hypochlorite solution) with ammonia solutions produces toxic/explosive ammonia trichloride vapors. Undergoes potentially violent or explosive reactions on contact with 1,2-dichloroethane (with liquid ammonia), boron halides, ethylene oxide (polymerization), perchlorates or strong oxidants (chromyl chloride, chromium trioxide, chromic acid, nitric acid, hydrogen peroxide, chlorates, fluorine, nitrogen oxide, liquid oxygen). Reacts with silver chloride, silver oxide, silver nitrate or silver azide to form the explosive silver nitride. May react with some heavy metal compounds (mercury, gold(III) chloride) to produce materials that may explode when dry. [Bretherick, 5th ed., 1995, p. 1553]. | | Health Hazard | Vapors cause irritation of eyes and respiratory tract. Liquid will burn skin and eyes. Poisonous; may be fatal if inhaled. Contact may cause burns to skin and eyes. Contact with liquid may cause frostbite. | | Fire Hazard | Mixing of ammonia with several chemicals can cause severe fire hazards and/or explosions. Ammonia in container may explode in heat of fire. Incompatible with many materials including silver and gold salts, halogens, alkali metals, nitrogen trichloride, potassium chlorate, chromyl chloride, oxygen halides, acid vapors, azides, ethylene oxide, picric acid and many other chemicals. Mixing with other chemicals and water. Hazardous polymerization may not occur. |
|