Chinese VersionChina Suppliers > Hubei new DE sheng material science and technology co., LTD. > What determines the pH value of the buffer solution Bicine?
- Search Product
-
-
- Region :China/Hubei
- Tel : +86-18971041571
- Fax :
- Email :vickyzhao@whdschem.com
- URL :
- Add :Guanggu United Science and Technology City C8, Ezhou City, Hubei Province
- Details for What determines the pH value of the buffer solution Bicine?
-
What determines the pH value of the buffer solution Bicine?
Category : Other Chemicals/Others

CAS NO : 150-25-4 EC NO : 205-755-1 MF : C6H17NO4 MW : 167.2035 Specification : White Powder Packing : 500g/bottle Product description : Biological buffer is usually a commonly used auxiliary reagent in biochemical detection and biological experiments, such as Bicine. Bicine buffer has the characteristics of maintaining the stability of system pH value, ensuring reaction progress, promoting enzyme activity, and stabilizing protein nucleic acid structure. One of the key roles is to buffer the changes in the acidity and alkalinity of the system. At this time, the pH value of Bicine buffer solution becomes particularly important. However, sometimes the pH value may be changed due to some factors. In this case, it is necessary to pay special attention to what determines its pH value? 1、 The pH value is determined by pKa The pH value of Bicine buffer solution is determined by the pKa and buffering ratio of the conjugated acid-base pairs that make up the buffer, but pKa plays a decisive role and buffering ratio has a smaller impact. Therefore, after preparing a buffer solvent, without determining which buffer to use, it is necessary to first search for the corresponding buffer range buffer based on the required pH value. The closer the pKa of the buffer is to the required pH value, the better. In addition, it is also necessary to pay attention to whether buffering agents have adverse reactions to the system reaction. If multiple buffering agents meet the pH requirements, a buffer solution with good solubility, non-toxic, harmless, strong stability, and easy storage can be selected. 2、 The pH value is determined by adjusting the buffer ratio If a buffering agent is determined, the change in its pH value is sometimes influenced by the adjustment of the buffering ratio. For example, an increase in the pH value of Bicine will increase the proportion of sodium hydroxide, while a decrease in pH will increase the proportion of Bicine. 3、 The pH value is determined by the concentration of buffer solution, ion strength, and osmotic pressure The higher the concentration of a buffer solution, the better its buffering effect and stronger buffering capacity. However, it should be noted that higher concentration is not necessarily better. When determining the preparation of a buffer solution, the pH value will also be affected by the total concentration, and the effects of ion strength and osmotic pressure on the reaction system need to be considered. The above three points are the key factors determining the pH range of Bicine buffer solution, and extra attention should be paid during use. Desheng Biochemical is a professional manufacturer of biological buffer solutions, such as commonly used Tris, Bicine, MOPS, CAPS, HEPES, etc., which are produced to meet most biological experimental needs. The company also has a large amount of stock available, which can be shipped on the same day according to customer needs. The quality is also highly praised by customers and exported overseas. If you have any needs for biological buffering agents, please click on the website for more information! Uses : Biological buffer Synonyms : Diethylolglycine;N,N-Bis(2-hydroxyethyl)glycine;BICINE = N,N-Bis(2-hydroxyethyl)glycine;Bicine, Molecular Biology Grade N,N-Bis(2-hydroxyethyl)glycine, Molecular Biology Grade;Bicine, ULTROL Grade;BICINE buffer Solution;BICINE, [N,N-Bis(2-hydroxyethyl)glycine];N,N-Di(2-hydroxyethyl)glycine;N,N-Di(2-hydroxyethyl)-glycine;N,N-dihydroxyethylglycine; Molecular Structure : 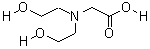
- more>>Other Products
-
- • Biological buffer 3- [N, N-di (hydroxyethyl) amino] -2-hydroxypropanesulfonic acid DIPSO
- • Luminol Sodium Salt
- • 4-Aminophthalhydrazide
- • acridinium ester DMAE-NHS
- • acridinium ester NSP-DMAE-NHS
- • Acridine hydrochloride NSP-SA
- • Acridine hydrochloride NSP-SA-NHS
- • NSP-SA-ADH
- • acridinium ester ME-DMAE-NHS TOOS; 3-(N-Ethyl-3-Methylanilino)-2-Hydroxypropanesulfonic Acid Sodium Salt
- • TOPS; Sodium 3-(N-Ethyl-3-Methylanilino)Propanesulfonate; N-Ethyl-N-Sulfopropyl-M-Toluidine Sodium Salt
- • ADOS Sodium 3-(Ethyl(3-Methoxyphenyl)Amino)-2-Hydroxypropane-1-Sulfonate Dihydrate
- • ADPS N-Ethyl-N-(3-Sulfopropyl)-3-Methoxyaniline Sodium Salt
- • ALPS N-Ethyl-N-(3-Sulfopropyl)Aniline Sodium Salt; Sodium 3-(Ethyl(Phenyl)Amino)Propane-1-Sulfonate; Sodium
- • DAOS; Sodium 3-((3,5-Dimethoxyphenyl)(Ethyl)Amino)-2-Hydroxypropane-1-Sulfonate
- • HDAOS; N-(2-Hydroxy-3-Sulfopropyl)-3,5-Dimethoxyaniline Sodium Salt
- • MADB N,N-Bis(4-Sulfobutyl)-3,5-Dimethylaniline Disodium Salt
- • MAOS N-Ethyl-N-(2-Hydroxy-3-Sulfopropyl)-3,5-Dimethylaniline Sodium Salt Monohydrate
- • DAB 3,3',4,4'-Biphenyltetramine Tetrahydrochloride