Chinese VersionChina Suppliers > Hubei new DE sheng material science and technology co., LTD. > What are the functions of EPPS buffer?
- Search Product
-
-
- Region :China/Hubei
- Tel : +86-18971041571
- Fax :
- Email :vickyzhao@whdschem.com
- URL :
- Add :Guanggu United Science and Technology City C8, Ezhou City, Hubei Province
- Details for What are the functions of EPPS buffer?
-
What are the functions of EPPS buffer?
Category : Other Chemicals/Others

CAS NO : 16052-06-5 EC NO : 240-198-8 MF : C9H20N2O4S MW : 252.3311 Specification : White Powder Packing : 500g/bottle Product description : EPPS buffer is a commonly used chemical reagent that plays an important role in biological science research and laboratory applications. Although it appears less frequently in the family of buffering agents, its effects cannot be ignored. It is often widely used in cell culture, proteomics, molecular biology, or other biochemical experiments. So below, we will provide a detailed introduction to its functions. 1、 PH regulation EPPS buffer can be used to regulate the acidity and alkalinity of solutions, keeping them within the desired pH range. Due to its good buffering ability, it can stably adjust pH values under neutral to alkaline conditions. Due to its pKa value of approximately 8.0, it is suitable for many biological experiments where the pH is close to neutral or slightly alkaline. 2、 Stability EPPS buffer has good stability, can maintain a relatively stable pH value of the solution, and is not easily affected by external conditions, making it a reliable buffer suitable for long-term experiments or stored samples. 3、 Application field 1. Cell culture: EPPS is commonly used in cell culture to provide a suitable growth environment and stable pH conditions, which contribute to the normal growth and metabolism of cells. 2. Proteomics: It can be used in protein electrophoresis and separation processes to provide a stable pH environment, ensuring the stability and separation efficiency of protein samples. 3. Molecular biology: It can also be used in molecular biology experiments such as DNA and RNA electrophoresis, hybridization, and amplification, providing a suitable environment to ensure the accuracy and reliability of experiments. 4、 Storage precautions EPPS buffer powder should be stored in a dry, dark place, away from moisture and direct sunlight. It should also be avoided from mixing with other chemicals to prevent possible reactions or mutual interference. EPPS buffer, as a commonly used chemical reagent, plays an important role in biological science research and laboratory applications due to its excellent pH regulation ability and stability, making it suitable for multiple fields. When using, it is not only necessary to pay attention to storage conditions, but researchers should also choose appropriate concentrations of EPPS according to experimental requirements and make reasonable adjustments to obtain better experimental results. As a professional manufacturer of biological buffering agents, Desheng offers a complete range of products for customers to choose from. The products are sold directly by the manufacturer with great price discounts, and sample testing is also provided. Once the test is qualified, the product can be shipped as a single order. If you have any relevant intentions, please click on the website to inquire about details and purchase! Uses : Biological buffer Synonyms : 3-[4-(2-Hydroxyethyl)-1-piperazine]propanesulfonic acid;4-(2-Hydroxyethyl)-1-piperazinepropanesulfonic acid;HEPPS N-(2-Hydroxyethyl)piperazine-N-3-propanesulfonic acid;N-(2-Hydroxyethyl)-N-(3-sulfopropyl)-piperazine;HEPPS, ULTROL Grade;HEPPS~4-(2-Hydroxyethyl)-1-piperazinepropanesulphonic acid;aEPPS;HEPPS;3-[4-(2-hydroxyethyl)piperazin-1-yl]propane-1-sulfonic acid;4-(2-Hydroxyethyl) piperazine-1-propanesulfonic acid; Molecular Structure : 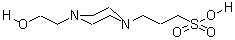
- more>>Other Products
-
- • Biological buffer 3- [N, N-di (hydroxyethyl) amino] -2-hydroxypropanesulfonic acid DIPSO
- • Luminol Sodium Salt
- • 4-Aminophthalhydrazide
- • acridinium ester DMAE-NHS
- • acridinium ester NSP-DMAE-NHS
- • Acridine hydrochloride NSP-SA
- • Acridine hydrochloride NSP-SA-NHS
- • NSP-SA-ADH
- • acridinium ester ME-DMAE-NHS TOOS; 3-(N-Ethyl-3-Methylanilino)-2-Hydroxypropanesulfonic Acid Sodium Salt
- • TOPS; Sodium 3-(N-Ethyl-3-Methylanilino)Propanesulfonate; N-Ethyl-N-Sulfopropyl-M-Toluidine Sodium Salt
- • ADOS Sodium 3-(Ethyl(3-Methoxyphenyl)Amino)-2-Hydroxypropane-1-Sulfonate Dihydrate
- • ADPS N-Ethyl-N-(3-Sulfopropyl)-3-Methoxyaniline Sodium Salt
- • ALPS N-Ethyl-N-(3-Sulfopropyl)Aniline Sodium Salt; Sodium 3-(Ethyl(Phenyl)Amino)Propane-1-Sulfonate; Sodium
- • DAOS; Sodium 3-((3,5-Dimethoxyphenyl)(Ethyl)Amino)-2-Hydroxypropane-1-Sulfonate
- • HDAOS; N-(2-Hydroxy-3-Sulfopropyl)-3,5-Dimethoxyaniline Sodium Salt
- • MADB N,N-Bis(4-Sulfobutyl)-3,5-Dimethylaniline Disodium Salt
- • MAOS N-Ethyl-N-(2-Hydroxy-3-Sulfopropyl)-3,5-Dimethylaniline Sodium Salt Monohydrate
- • DAB 3,3',4,4'-Biphenyltetramine Tetrahydrochloride