Chinese VersionChina Suppliers > Hubei new DE sheng material science and technology co., LTD. > The application principle of EDTA dipotassium in blood routine
- Search Product
-
-
- Region :China/Hubei
- Tel : +86-18971041571
- Fax :
- Email :vickyzhao@whdschem.com
- URL :
- Add :Guanggu United Science and Technology City C8, Ezhou City, Hubei Province
- Details for The application principle of EDTA dipotassium in blood routine
-
The application principle of EDTA dipotassium in blood routine
Category : Other Chemicals/Others

CAS NO : 25102-12-9 EC NO : MF : C10H12K2N2O8 MW : 366.4086 Specification : White Powder Packing : 500g/bottle Product description : When going to the hospital for a physical examination, doctors often prescribe blood routine tests, which are closely related to our daily lives. Today, we will talk about the application principles of blood routine and EDTA potassium in clinical blood routine tests. Blood routine is a test that determines blood status and disease by monitoring changes in the number and distribution of blood cells. Multiple indicators on the blood routine test sheet are sensitive to many pathological changes in the human body. Therefore, when conducting blood routine tests, the number of white blood cells, red blood cells, platelets, and hemoglobin can be checked to detect early signs of systemic diseases. For example, diagnosing whether there is a blood disease, anemia, and the hematopoietic function of the bone marrow. Blood routine is a common blood test item. When drawing blood, in order to ensure that the blood does not coagulate, blood collection vessels containing anticoagulants are currently used. The commonly used anticoagulant is EDTA-K2, which has good anticoagulant effects and minimal impact on the morphology of blood cells. To understand the anticoagulant principle of EDTA dipotassium, it is necessary to clarify the four common steps of blood coagulation: 1. The formation of prothrombin activators. 2. Subsequently, prothrombin is transformed into an active thrombin with the participation of calcium ions and phospholipid membranes. 3. Then form fibrinogen, which is converted from soluble fibrinogen to insoluble fibrinogen under the action of thrombin. 4. After the generation of fibrin, it will adsorb thrombin and form local blood clots. This is the pathway through which blood coagulation occurs. EDTA dipotassium is a chelating agent in the form of a white crystalline powder. Due to its strong affinity for calcium ions, it can chelate with calcium ions to block the formation of prothrombin and form thrombin. This means that the second step of the blood coagulation process mentioned above is suspended, and the subsequent coagulation process cannot continue, which can play a role in blood anticoagulation. EDTA dipotassium is used in conjunction with whole blood analyzers to prepare anticoagulant tubes, anticoagulants, and vacuum anticoagulant tubes. Desheng is a well-established manufacturer of blood collection reagents. Its anticoagulant EDTA dipotassium has a unit packaging volume of 500g/bottle and a shelf life of 3 years. It has served many domestic and foreign customers, and the repurchase rate is also very high, which shows that its quality is guaranteed. Uses : Blood collection additive Synonyms : EDTA-2K•2H20;2K;EDTA, Dipotassium Salt;Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid, dipotassium salt;Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid, dipotassium salt dihydrate;Ethylenediamine-N,N,N',N'-tetraacetic acid, dipotassium salt, dihydrate;Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid,dipotassium salt dihydrate;EDTA-2K·2H20;acetate, 2,2',2'',2'''-(1,2-ethanediyldinitrilo)tetrakis-, potassium salt (1:2);Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid dipotassium salt dihydrate;Ethylenedinitrilotetraacetic acid dipotassium salt dihydrate; Molecular Structure : 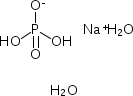
- more>>Other Products
-
- • Biological buffer 3- [N, N-di (hydroxyethyl) amino] -2-hydroxypropanesulfonic acid DIPSO
- • Luminol Sodium Salt
- • 4-Aminophthalhydrazide
- • acridinium ester DMAE-NHS
- • acridinium ester NSP-DMAE-NHS
- • Acridine hydrochloride NSP-SA
- • Acridine hydrochloride NSP-SA-NHS
- • NSP-SA-ADH
- • acridinium ester ME-DMAE-NHS TOOS; 3-(N-Ethyl-3-Methylanilino)-2-Hydroxypropanesulfonic Acid Sodium Salt
- • TOPS; Sodium 3-(N-Ethyl-3-Methylanilino)Propanesulfonate; N-Ethyl-N-Sulfopropyl-M-Toluidine Sodium Salt
- • ADOS Sodium 3-(Ethyl(3-Methoxyphenyl)Amino)-2-Hydroxypropane-1-Sulfonate Dihydrate
- • ADPS N-Ethyl-N-(3-Sulfopropyl)-3-Methoxyaniline Sodium Salt
- • ALPS N-Ethyl-N-(3-Sulfopropyl)Aniline Sodium Salt; Sodium 3-(Ethyl(Phenyl)Amino)Propane-1-Sulfonate; Sodium
- • DAOS; Sodium 3-((3,5-Dimethoxyphenyl)(Ethyl)Amino)-2-Hydroxypropane-1-Sulfonate
- • HDAOS; N-(2-Hydroxy-3-Sulfopropyl)-3,5-Dimethoxyaniline Sodium Salt
- • MADB N,N-Bis(4-Sulfobutyl)-3,5-Dimethylaniline Disodium Salt
- • MAOS N-Ethyl-N-(2-Hydroxy-3-Sulfopropyl)-3,5-Dimethylaniline Sodium Salt Monohydrate
- • DAB 3,3',4,4'-Biphenyltetramine Tetrahydrochloride