Chinese VersionChina Suppliers > Hubei new DE sheng material science and technology co., LTD. > TOPS determination of free fatty acids using chromogenic substrates
- Search Product
-
-
- Region :China/Hubei
- Tel : +86-18971041571
- Fax :
- Email :vickyzhao@whdschem.com
- URL :
- Add :Guanggu United Science and Technology City C8, Ezhou City, Hubei Province
- Details for TOPS determination of free fatty acids using chromogenic substrates
-
TOPS determination of free fatty acids using chromogenic substrates
Category : Other Chemicals/Others

CAS NO : 40567-80-4 EC NO : MF : C12H18NNaO3S MW : 279.331 Specification : White Powder Packing : 500g/bottle Product description : TOPS, a chromogenic substrate, belongs to a novel Trinder's reagent, fully known as N-ethyl-N - (3-sulfopropyl) -3-methylaniline sodium salt, CAS number 40567-80-4. It is one of the important raw materials in the biochemical reagent kit, which can be used for the determination of free fatty acids, cholesterol, uric acid and other indicators. This article introduces the TOPS method for determining fatty acids. TOPS determination of free fatty acids Determination of free fatty acids Free fatty acids (FFA) in serum refer to non esterified fatty acids (NEFAs), which have a low content in serum because the body's fat is mainly stored in the form of triglycerides. For the detection of a small amount of serum samples in vacuum blood collection vessels, due to the low FFA content, sensitive methods need to be used for detection, and interference from fatty acids produced by fat hydrolysis should be avoided. Therefore, highly sensitive TOPS reagents and catalase spectrophotometry can be used to determine FFA. Determination of FFA by TOPS enzyme spectrophotometry This detection method has three reaction steps: free fatty acids (FFA or NEFA) react with excess CoA to form acyl CoA under the action of acetyl CoA synthase (ACS), and react with oxygen under the action of acetyl CoA oxidase (ACO) to produce 2,3-trans-enoyl CoA and hydrogen peroxide. The content of FFA can be determined by using the Trinder reaction to detect hydrogen peroxide. Precautions for TOPS determination of FFA 1. Excessive CoA in the TOPS determination of FFA experiment can interfere with the reaction between hydrogen peroxide and Trinder chromogen, resulting in a lower overall detection result. N-ethylmaleimide (NEM) can be used to remove excess CoA, but it should be noted that the stability of NEM is very limited, only for one week. 2. The substrate specificity of acetyl CoA synthase and acetyl CoA oxidase used for different free fatty acids varies, resulting in differences in the measurement results. Different enzyme sources have different substrate specificity for free fatty acids with different C-chain lengths, that is, different reaction abilities. Human serum contains six types of FFA, and only enzymes with high specificity for their reactions can ensure no difference in the test results. It is understood that some test kits may also use other color reagents such as TOOS to determine free fatty acids. However, according to customer feedback, TOPS has more advantages. It is significantly less affected by CoA than TOOS, and its molar absorption coefficient is only slightly lower than TOOS. Therefore, Desheng suggests using TOPS to determine FFA. Uses : The New trinder's reagent Synonyms : 3-(N-Ethyl-3-methylanilino)propanesulfonic acid sodium salt;SODIUM N-ETHYL-N-(3-SULFOPROPYL)-M-TOLUIDINE;SODIUM 3-(N-ETHYL-3-METHYLANILINO)PROPANESULFONATE;N-ETHYL-N-SULPHOPROPYL-M-TOLUIDINE, SODIUM SALT;N-ETHYL-N-SULFOPROPYL-3-TOLUIDINE SODIUM SALT;N-ETHYL-N-SULFOPROPYL-M-TOLUIDINE;N-ETHYL-N-SULFOPROPYL-M-TOLUIDINE SODIUM SALT;TOPS, SODIUM SALT;N-ethyl-N-(3-sulfopropyl)-m-toluidine, sodium salt;N-Ethyl-N-(3-sulfopropyl)-3-methylaniline sodium salt;1-[ethyl(3-methylphenyl)amino]propane-1-sulfonic acid;sodium 3-[ethyl(3-methylphenyl)amino]propane-1-sulfonate;3-[Ethyl(3-methyIphenyl)amino]-1-propane sulfonic acid, Sodium Salt; Molecular Structure : 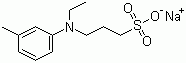
- more>>Other Products
-
- • Biological buffer 3- [N, N-di (hydroxyethyl) amino] -2-hydroxypropanesulfonic acid DIPSO
- • Luminol Sodium Salt
- • 4-Aminophthalhydrazide
- • acridinium ester DMAE-NHS
- • acridinium ester NSP-DMAE-NHS
- • Acridine hydrochloride NSP-SA
- • Acridine hydrochloride NSP-SA-NHS
- • NSP-SA-ADH
- • acridinium ester ME-DMAE-NHS TOOS; 3-(N-Ethyl-3-Methylanilino)-2-Hydroxypropanesulfonic Acid Sodium Salt
- • TOPS; Sodium 3-(N-Ethyl-3-Methylanilino)Propanesulfonate; N-Ethyl-N-Sulfopropyl-M-Toluidine Sodium Salt
- • ADOS Sodium 3-(Ethyl(3-Methoxyphenyl)Amino)-2-Hydroxypropane-1-Sulfonate Dihydrate
- • ADPS N-Ethyl-N-(3-Sulfopropyl)-3-Methoxyaniline Sodium Salt
- • ALPS N-Ethyl-N-(3-Sulfopropyl)Aniline Sodium Salt; Sodium 3-(Ethyl(Phenyl)Amino)Propane-1-Sulfonate; Sodium
- • DAOS; Sodium 3-((3,5-Dimethoxyphenyl)(Ethyl)Amino)-2-Hydroxypropane-1-Sulfonate
- • HDAOS; N-(2-Hydroxy-3-Sulfopropyl)-3,5-Dimethoxyaniline Sodium Salt
- • MADB N,N-Bis(4-Sulfobutyl)-3,5-Dimethylaniline Disodium Salt
- • MAOS N-Ethyl-N-(2-Hydroxy-3-Sulfopropyl)-3,5-Dimethylaniline Sodium Salt Monohydrate
- • DAB 3,3',4,4'-Biphenyltetramine Tetrahydrochloride