Chinese VersionChina Suppliers > Hubei new DE sheng material science and technology co., LTD. > The role of HEPES in cell culture process
- Search Product
-
-
- Region :China/Hubei
- Tel : +86-18971041571
- Fax :
- Email :vickyzhao@whdschem.com
- URL :
- Add :Guanggu United Science and Technology City C8, Ezhou City, Hubei Province
- Details for The role of HEPES in cell culture process
-
The role of HEPES in cell culture process
Category : Other Chemicals/Others

CAS NO : 7365-45-9 EC NO : 230-907-9 MF : C8H19N2O4S MW : 239.3119 Specification : White Powder Packing : 500g/bottle Product description : The role of HEPES in cell culture process Cell culture is a commonly used biological research method that simulates the in vivo environment to allow cells to grow and reproduce in vitro. Maintaining an appropriate pH value of the culture medium is crucial for the growth and reproduction of cells during the cell culture process. HEPES, as a commonly used buffer, plays an important role in this process. 1、 Product Introduction The chemical name is 4-hydroxyethylpiperazine ethanesulfonic acid, which is a weak acid that can act as a biological buffer to maintain the stability of the pH value of the experimental system. Its molecular formula is C8H18N2O4S, and its CAS number is 7365-45-9. The appearance is white crystalline powder with good solubility, which is soluble in water and increases with temperature. 2、 Role in cell culture Maintain stable pH value of the culture medium During cell growth and metabolism, acidic substances such as lactic acid and carbon dioxide are produced, which can cause a decrease in the pH value of the culture medium. As a weak acid, HEPES can neutralize hydrogen ions in the culture medium, resist pH changes, maintain pH within an appropriate range, and provide a stable environment for cell growth and reproduction. Due to the independence of buffering capacity from CO2 concentration, it is an ideal buffer for maintaining culture pH when cell culture requires long-term operations outside of CO2. Non toxic side effects on cells Non toxic side effects on cells, suitable for various cell culture experiments. High concentrations can cause cytotoxicity, so when there is significant toxicity to specific cell lines or primary cell cultures, the concentration of this organic buffer should be reduced. Good stability It can remain stable for a long time at room temperature and is not easily decomposed or spoiled. However, when exposed to light, hydrogen peroxide is produced, which may be toxic to cultured cells or other biologically active objects. Therefore, when using it, it should be done in a dark environment as much as possible. 3、 Preparation method of buffer solution The preparation method is as follows: Weigh the required amount of HEPES, add an appropriate amount of distilled water to dissolve it, then adjust the pH value to the desired range with NaOH or HCl, and finally add distilled water to the required volume. It should be noted that when preparing buffer solution, appropriate concentration and pH range should be selected according to experimental needs. Generally speaking, lower concentrations are not sufficient to control pH fluctuations, while higher concentrations are usually toxic. Therefore, it is necessary to optimize the selection according to the experimental requirements. 4、 Summary HEPES, as a commonly used buffer, plays an important role in cell culture. It can maintain the pH stability of the culture medium, has no toxic side effects on cells, and has good stability. When using, it is important to avoid exposure to light to prevent the production of hydrogen peroxide, which can cause toxicity to cells. In addition, it is necessary to select an appropriate concentration and pH range for optimization based on experimental requirements. In summary, the use of HEPES helps to improve the efficiency and stability of cell culture experiments. Uses : Biological buffer Synonyms : 2-[4-(2-Hydroxyethyl)-1-piperazine]ethanesulfonic acid;4-(2-Hydroxyethyl)-1-piperazineethanesulphonic acid;N-(2-Hydroxyethyl)piperazine-N-(2-ethanesulfonic acid);HEPES;N-(2-Hydroxyethyl)piperazine-N-(2-ethanesulfonic acid), Tissue Culture Tested;N-(2-Hydroxyethyl)piperazine-N-(2-ethanesulfonic acid), Molecular Biology Grade;HEPES;4-(2-hydroxyethyl)-1-piperazineethanesulfonicacid;4-(2-HYDROXYETHYL)-1-PIPERAZINEETHANESULFONIC ACID;4-(2-HYDROXYETHYL)PIPERAZINE-1-ETHANESULFONIC ACID;2-[4-(2-HYDROXYETHYL)-1-PIPERAZINYL]ETHANESULFONIC ACID;LABOTEST-BB LT00138109;LABOTEST-BB LT00233156;HEPES;2-[4-(Hydroxyethyl)-1-piperazinyl]ethane sulfonic acid;2-[4-(2-hydroxyethyl)piperazin-4-ium-1-yl]ethanesulfonate;2-[4-(2-hydroxyethyl)piperazinediium-1-yl]ethanesulfonate;N-(2-Hydroxyethyl)piperazine-N'-(2-ethanesulfonic acid);4-(2-Hydroxyethy1)-1-piperazineethanesulfonic acid;N-(2-Hydroxyethyl)-piperazine-N'-2-ethanesulfonic acid;N-2-Hydroxyethylpiperazine-N-2-ethanesulfonic acid; Molecular Structure : 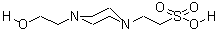
- more>>Other Products
-
- • Biological buffer 3- [N, N-di (hydroxyethyl) amino] -2-hydroxypropanesulfonic acid DIPSO
- • Luminol Sodium Salt
- • 4-Aminophthalhydrazide
- • acridinium ester DMAE-NHS
- • acridinium ester NSP-DMAE-NHS
- • Acridine hydrochloride NSP-SA
- • Acridine hydrochloride NSP-SA-NHS
- • NSP-SA-ADH
- • acridinium ester ME-DMAE-NHS TOOS; 3-(N-Ethyl-3-Methylanilino)-2-Hydroxypropanesulfonic Acid Sodium Salt
- • TOPS; Sodium 3-(N-Ethyl-3-Methylanilino)Propanesulfonate; N-Ethyl-N-Sulfopropyl-M-Toluidine Sodium Salt
- • ADOS Sodium 3-(Ethyl(3-Methoxyphenyl)Amino)-2-Hydroxypropane-1-Sulfonate Dihydrate
- • ADPS N-Ethyl-N-(3-Sulfopropyl)-3-Methoxyaniline Sodium Salt
- • ALPS N-Ethyl-N-(3-Sulfopropyl)Aniline Sodium Salt; Sodium 3-(Ethyl(Phenyl)Amino)Propane-1-Sulfonate; Sodium
- • DAOS; Sodium 3-((3,5-Dimethoxyphenyl)(Ethyl)Amino)-2-Hydroxypropane-1-Sulfonate
- • HDAOS; N-(2-Hydroxy-3-Sulfopropyl)-3,5-Dimethoxyaniline Sodium Salt
- • MADB N,N-Bis(4-Sulfobutyl)-3,5-Dimethylaniline Disodium Salt
- • MAOS N-Ethyl-N-(2-Hydroxy-3-Sulfopropyl)-3,5-Dimethylaniline Sodium Salt Monohydrate
- • DAB 3,3',4,4'-Biphenyltetramine Tetrahydrochloride