Chinese VersionChina Suppliers > Hubei new DE sheng material science and technology co., LTD. > HEPES buffer for cell culture
- Search Product
-
-
- Region :China/Hubei
- Tel : +86-18971041571
- Fax :
- Email :vickyzhao@whdschem.com
- URL :
- Add :Guanggu United Science and Technology City C8, Ezhou City, Hubei Province
- Details for HEPES buffer for cell culture
-
HEPES buffer for cell culture
Category : Other Chemicals/Others

CAS NO : 7365-45-9 EC NO : 230-907-9 MF : C8H19N2O4S MW : 239.3119 Specification : White Powder Packing : 500g/bottle Product description : Cell culture is one of the key technologies in biological and biomedical research, used to study various types of cells, including bacteria, yeast, mammalian cells, etc. To ensure the growth and reproduction of cells under culture conditions, it is necessary to provide an appropriate environment, including suitable culture media and buffer solutions. Among them, HEPES (4-hydroxyethylpiperazine ethanesulfonic acid) is a commonly used buffer and is widely used in cell culture. The importance of HEPES buffer in cell culture Maintaining an appropriate pH value is crucial in cell culture, as changes in pH may have negative effects on cell metabolism, enzyme activity, and growth. HEPES is known for its excellent buffering performance, which can quickly stabilize the pH of the culture medium within a stable range under cell culture conditions without interfering with normal cell growth. Application of HEPES buffer in cell culture 1. Reducing the toxicity of culture media: During cell culture, some chemicals may have toxic effects on cells. HEPES buffer can reduce the toxicity of these substances and improve cell survival rate. 2. Promoting cell adhesion growth: During cell culture, cell adhesion growth can maintain normal cell morphology and function. HEPES buffer can promote cell growth, improve cell proliferation ability and survival rate. 3. Maintaining the electrical balance of the intracellular and extracellular environment: The electrical balance of the intracellular and extracellular environment is crucial for the normal physiological function of cells. HEPES buffer can maintain the electrical balance of the intracellular and extracellular environment, ensuring the normal physiological function of cells. 4. As a metal ion chelating agent: HEPES buffer can chelate metal ions in the culture medium, reduce the toxic effect of metal ions on cells, and ensure the concentration of essential metal ions in the culture medium. 5. Application in suspension cell culture: For suspension cell lines, HEPES buffer can provide a stable pH environment and maintain the intracellular and extracellular environment, promoting cell growth and division. At the same time, it can also serve as a metal ion chelating agent to reduce the toxic effect of metal ions on cells. 6. Application in serum-free cell culture: In serum-free cell culture, HEPES buffer can reduce the toxic effects of other chemicals in the culture medium, promote cell proliferation ability, and ensure the concentration of metal ions in the culture medium. 7. Application in stem cell culture: Stem cells have the ability to self renew and differentiate in multiple directions, which is helpful for regenerative medicine. HEPES buffer can provide a stable pH environment, reduce the side effects of other chemicals in the culture medium, and promote the growth of stem cells. 8. Application in tumor cell culture: In tumor cell culture, HEPES buffer reduces the resistance of tumor cells to chemotherapy drugs and enhances the killing effect of chemotherapy drugs on tumor cells. 9. Application in immune cell culture: Promoting the activation and proliferation of immune cells in immune cell culture. In addition, HEPES can also affect the biological function of immune cells by adjusting parameters such as osmotic pressure and ion strength of the culture medium. Uses : Biological buffer Synonyms : 2-[4-(2-Hydroxyethyl)-1-piperazine]ethanesulfonic acid;4-(2-Hydroxyethyl)-1-piperazineethanesulphonic acid;N-(2-Hydroxyethyl)piperazine-N-(2-ethanesulfonic acid);HEPES;N-(2-Hydroxyethyl)piperazine-N-(2-ethanesulfonic acid), Tissue Culture Tested;N-(2-Hydroxyethyl)piperazine-N-(2-ethanesulfonic acid), Molecular Biology Grade;HEPES;4-(2-hydroxyethyl)-1-piperazineethanesulfonicacid;4-(2-HYDROXYETHYL)-1-PIPERAZINEETHANESULFONIC ACID;4-(2-HYDROXYETHYL)PIPERAZINE-1-ETHANESULFONIC ACID;2-[4-(2-HYDROXYETHYL)-1-PIPERAZINYL]ETHANESULFONIC ACID;LABOTEST-BB LT00138109;LABOTEST-BB LT00233156;HEPES;2-[4-(Hydroxyethyl)-1-piperazinyl]ethane sulfonic acid;2-[4-(2-hydroxyethyl)piperazin-4-ium-1-yl]ethanesulfonate;2-[4-(2-hydroxyethyl)piperazinediium-1-yl]ethanesulfonate;N-(2-Hydroxyethyl)piperazine-N'-(2-ethanesulfonic acid);4-(2-Hydroxyethy1)-1-piperazineethanesulfonic acid;N-(2-Hydroxyethyl)-piperazine-N'-2-ethanesulfonic acid;N-2-Hydroxyethylpiperazine-N-2-ethanesulfonic acid; Molecular Structure : 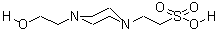
- more>>Other Products
-
- • Biological buffer 3- [N, N-di (hydroxyethyl) amino] -2-hydroxypropanesulfonic acid DIPSO
- • Luminol Sodium Salt
- • 4-Aminophthalhydrazide
- • acridinium ester DMAE-NHS
- • acridinium ester NSP-DMAE-NHS
- • Acridine hydrochloride NSP-SA
- • Acridine hydrochloride NSP-SA-NHS
- • NSP-SA-ADH
- • acridinium ester ME-DMAE-NHS TOOS; 3-(N-Ethyl-3-Methylanilino)-2-Hydroxypropanesulfonic Acid Sodium Salt
- • TOPS; Sodium 3-(N-Ethyl-3-Methylanilino)Propanesulfonate; N-Ethyl-N-Sulfopropyl-M-Toluidine Sodium Salt
- • ADOS Sodium 3-(Ethyl(3-Methoxyphenyl)Amino)-2-Hydroxypropane-1-Sulfonate Dihydrate
- • ADPS N-Ethyl-N-(3-Sulfopropyl)-3-Methoxyaniline Sodium Salt
- • ALPS N-Ethyl-N-(3-Sulfopropyl)Aniline Sodium Salt; Sodium 3-(Ethyl(Phenyl)Amino)Propane-1-Sulfonate; Sodium
- • DAOS; Sodium 3-((3,5-Dimethoxyphenyl)(Ethyl)Amino)-2-Hydroxypropane-1-Sulfonate
- • HDAOS; N-(2-Hydroxy-3-Sulfopropyl)-3,5-Dimethoxyaniline Sodium Salt
- • MADB N,N-Bis(4-Sulfobutyl)-3,5-Dimethylaniline Disodium Salt
- • MAOS N-Ethyl-N-(2-Hydroxy-3-Sulfopropyl)-3,5-Dimethylaniline Sodium Salt Monohydrate
- • DAB 3,3',4,4'-Biphenyltetramine Tetrahydrochloride